There's a lot of talk about NMN and NR (precursors for NAD+) within the longevity space. Learn the differences between NMN and NR and which one is right for you.
There's a lot of talk about NMN and NR (precursors for NAD+) within the longevity space. Learn the differences between NMN and NR and which one is right for you.
Can scents really impact cognitive performance? Discover the intriguing link between incorporating a nightly aromatherapy and its impact on cognitive performance, assessed through a standard memory test.
Could getting more sleep help you lose weight? A 2022 study set out to answer that question. Here’s what you need to know.
Psychobiotics are probiotics and prebiotics for the brain. But can psychobiotics really influence cognition, stress responses, mood, and emotional regulation? Read to learn more.
Brain fog is not a medical condition; it’s a clue that suggests there may be something interfering with your mental performance. Here are five factors that contribute to brain fog, according to a neuroscientist.
Everyone can benefit from acquiring a general understanding of our innate Reticular Activating System, as it is central to how, when, and why we focus on something.
Cellular senescence is a state of irreversible growth arrest that turns functional cells into zombie cells. These senescent cells occur in all types of tissues and organs and the skin is no exception.
Deep dive into the main mechanisms of functional and structural brain plasticity.
Science-backed tools and techniques to help you harness neuroplasticity and improve cognitive performance.
There is an organ that we often take for granted and whose importance should probably be more acknowledged: the skin.
This study aimed to assess whether Qualia Skin, by providing skin nourishment from within and supporting comprehensive skin health and healthy skin aging, would change participant satisfaction and self-ratings of aspects of the skin’s feel and appearance.
Understanding the main aspects of skin health, the major processes and pathways of healthy skin physiology, and the mechanisms of skin aging is essential to learning how to keep the skin healthy and youthful.

The best way to understand how to keep the skin healthy and youthful is by understanding what are the factors that impact skin health and aging, which is what we’ll explore in this article.
The skin is a special organ that combines the body’s major systems: circulatory, nervous, muscular, immune, endocrine. It is a barrier that protects us against the threats in our environment, but it is also a sensory organ that allows us to perceive the outside world. Read on to understand both the structure and function of the skin.

Selectively eliminating dysfunctional mitochondria (mitophagy) and replacing them with new mitochondria (mitochondrial biogenesis) helps us stay biologically younger. But what exactly are the functions of mitochondria and how does mitochondrial health affect aging?
Being fully aware of the hurdles of screen time—we spend as much time looking at screens as anyone else—we wanted to create a product that would support and protect the health, resistance, and resilience of the visual system. We designed Qualia Vision to help our eyes cope with the challenges of the digital age hose a set of ingredients that could support visual health and performance.
Learn what blue light is and if it’s bad for our eyes.
Nootropics are substances that enhance cognitive function and performance. Nootropics have become increasingly popular in recent years but you might still have questions about the science surrounding nootropics. If so, this article is for you.
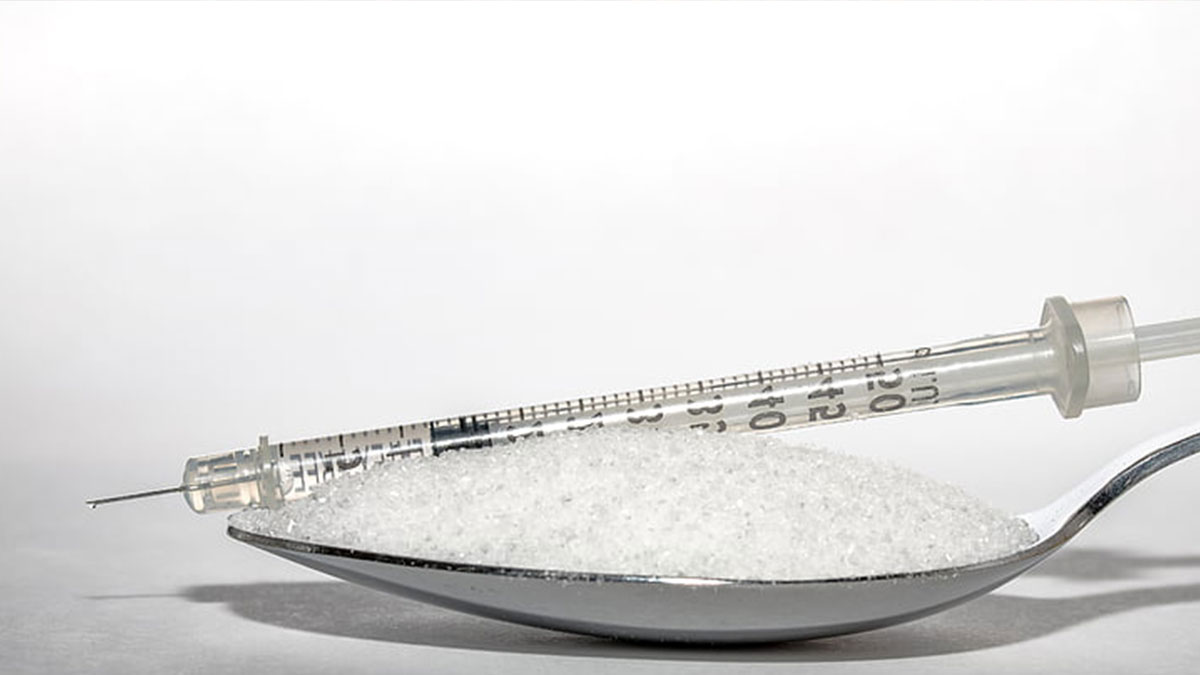
Insulin is a hormone produced by beta cells in the pancreas with a central role in the regulation of metabolism and cell energy reserves. The major metabolic action of insulin is to regulate blood glucose levels and to promote the storage of energy substrates as macromolecules that can be mobilized between meals or in contexts of high energy demand.
Oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) is the major pathway of ATP production. ATP is the energy-rich molecule that powers cellular processes that require energy input. OXPHOS occurs in mitochondria and uses energy extracted in the metabolism of cellular fuels, particularly in glycolysis, fatty acid oxidation, and the citric acid cycle, to power the production of ATP.
The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a circular loop rotating through eight organic acid intermediates (e.g., citrate, malate, oxaloacetate). This cycle plays a critical role in moving cell energy production forward, because it is the first pathway of the final stage of energy extraction from nutrients, in which carbon units are fully oxidized. The intermediate products formed in this cycle are also used to build molecules including proteins, DNA, and RNA.
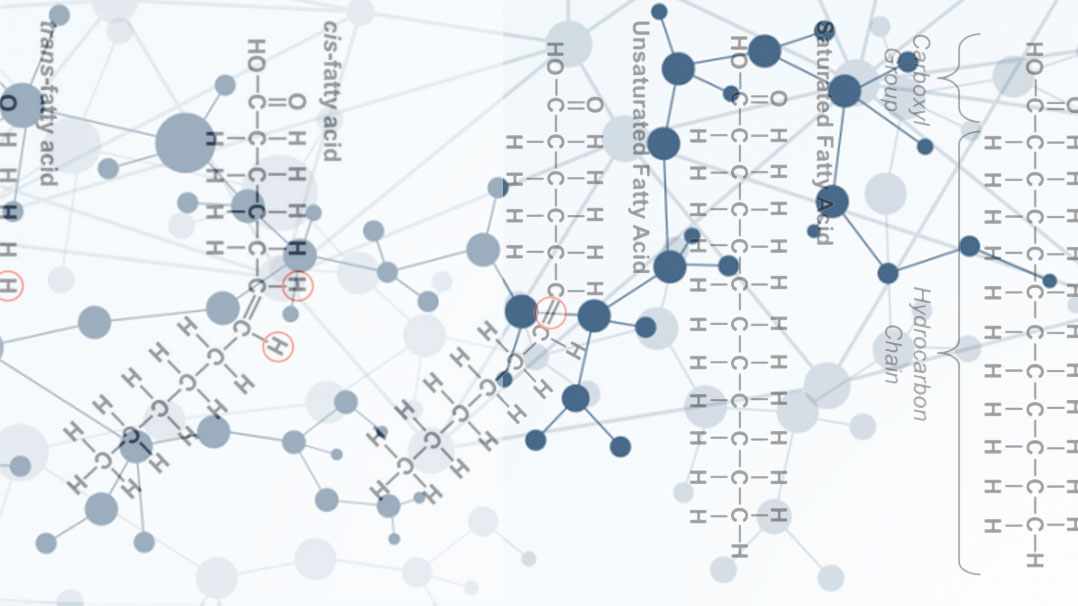
Fatty acids are an important fuel for the generation of cell energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Fatty acid oxidation, also known as beta-oxidation, is the metabolic pathway of fatty acid breakdown for energy production. Fatty acids are the primary source of energy for the heart (i.e., the cardiac muscle) and skeletal muscle during rest or moderate physical activity.
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that breaks down the carbohydrate glucose to produce cell energy in the form of ATP. Glycolysis generates ATP directly, as a product of the pathway’s chemical reactions, and indirectly, using energy generated by electrons extracted from the chemical bonds of glucose. In the human body, glucose is the preferred fuel for the vast majority of cells.